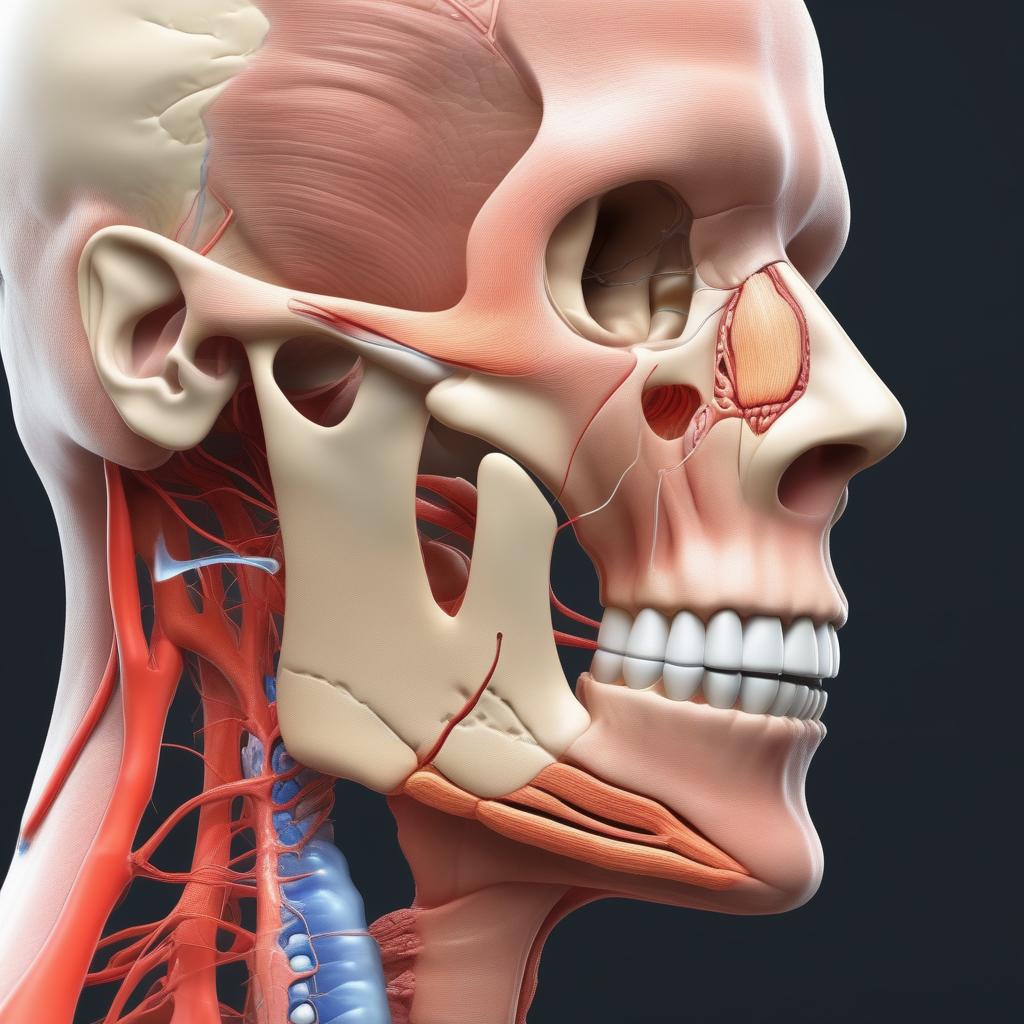
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve and is responsible for providing sensation to the face, as well as controlling the muscles used for chewing. It is named the trigeminal nerve because it has three branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). These branches innervate different areas of the face, such as the forehead, cheeks, and jaw.
Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects the trigeminal nerve and results in episodes of severe pain in the face. The pain is often described as sharp, stabbing, or electric shock-like and can be triggered by simple activities such as brushing teeth or talking. Trigeminal neuralgia can be debilitating and significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia may include medications such as anticonvulsants or nerve blocks, but in severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve the pain. There are also alternative treatments such as acupuncture or biofeedback that some people find helpful in managing their symptoms. Overall, trigeminal neuralgia is a challenging condition to live with, but with proper management and support, individuals can find relief from their symptoms.